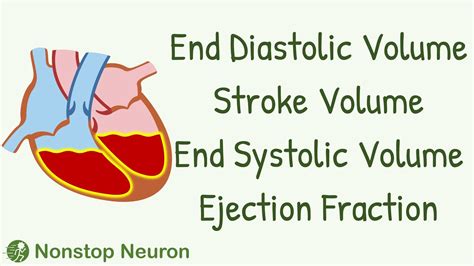
lv end diastolic volume | Lv stroke volume 4c al lv end diastolic volume Results: The normal ranges for LV end-diastolic volume measurements after adjustment to body surface area (BSA) were 62-120 ml for males and 58-103 ml for females. LV mass indexed to . CHRONO.LV is an exclusive online catalogue of Swiss watches with over 10 years of experience in watch sales.
0 · what is Lv diastolic volume
1 · stroke volume vs end diastolic
2 · end diastolic volume vs systolic
3 · end diastolic volume chart
4 · end dialysis volume chart
5 · Lv stroke volume 4c al
6 · Lv stroke volume 2d teich
7 · Lv diastolic volume normal range
Cimarron features one, two, and three bedroom apartments in Las Vegas, Nevada for you to choose from based on your needs + lifestyle. Don't wait to explore our community! All dimensions and square footage are approximate. Actual amenities and specifications may vary in dimension or detail.
End-diastolic volume is a useful indicator of a person’s heart health. Doctors use end-diastolic volume to estimate preload and calculate the heart’s stroke volume and ejection fraction.Normal (reference) values for echocardiography, for all measurements, according to AHA, ACC and ESC, with calculators, reviews and e-book.
In cardiovascular physiology, end-diastolic volume (EDV) is the volume of blood in the right or left ventricle at end of filling in diastole which is amount of blood present in ventricle at the end of diastole. Because greater EDVs cause greater distention of the ventricle, EDV is often used synonymously with preload, which refers to the length of the sarcomeres in cardiac muscle prior to contraction (systole). An increase in EDV increases the preload on the heart and, through the Frank-Starling mechanismDetermining the left ventricular (LV) end-diastolic volume index (EDVI) is essential to evaluating LV function. LV EDVI—the volume of blood in the LV at end load filling indexed for body .Results: The normal ranges for LV end-diastolic volume measurements after adjustment to body surface area (BSA) were 62-120 ml for males and 58-103 ml for females. LV mass indexed to .
The end-diastolic volume is an essential parameter used for the assessment of cardiac function, namely the calculation of the respective stroke volumes and ejection fraction .ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC ASSESSMENT OF LV FILLING PRESSURES AND DIASTOLIC DYSFUNCTION GRADE. The key variables recommended for assessment of LV diastolic .
The LV volume point on the loop is the end-systolic (i.e., residual) volume (ESV). When the LVP falls below the left atrial pressure, the mitral valve opens (point 4) and the ventricle begins to fill.
The optimal view for measuring the left ventricular diastolic area is the left ventricular short axis view from the mid transgastric acoustic window. This view has been shown to be predictive of . Left ventricular end-diastolic volume is the amount of blood in the heart’s left ventricle just before the heart contracts. While the right ventricle also has an end-diastolic volume,. End-diastolic volume is a useful indicator of a person’s heart health. Doctors use end-diastolic volume to estimate preload and calculate the heart’s stroke volume and ejection fraction.
Normal (reference) values for echocardiography, for all measurements, according to AHA, ACC and ESC, with calculators, reviews and e-book.
In cardiovascular physiology, end-diastolic volume (EDV) is the volume of blood in the right or left ventricle at end of filling in diastole which is amount of blood present in ventricle at the end of diastole. [1]Determining the left ventricular (LV) end-diastolic volume index (EDVI) is essential to evaluating LV function. LV EDVI—the volume of blood in the LV at end load filling indexed for body surface area (ml/m 2)—may be quantified, either manually or automatically, using cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) software.Results: The normal ranges for LV end-diastolic volume measurements after adjustment to body surface area (BSA) were 62-120 ml for males and 58-103 ml for females. LV mass indexed to BSA ranged from 50-86 g for males and 36-72 g for females. The end-diastolic volume is an essential parameter used for the assessment of cardiac function, namely the calculation of the respective stroke volumes and ejection fraction and the estimation of left or right ventricular preload. It has a central role in the diagnosis of many cardiac conditions.
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC ASSESSMENT OF LV FILLING PRESSURES AND DIASTOLIC DYSFUNCTION GRADE. The key variables recommended for assessment of LV diastolic function grade include mitral flow velocities, mitral annular e0 ve-locity, E/e0 ratio, peak velocity of TR jet, and LA maximum volume index (Figure 8B).
The LV volume point on the loop is the end-systolic (i.e., residual) volume (ESV). When the LVP falls below the left atrial pressure, the mitral valve opens (point 4) and the ventricle begins to fill.The optimal view for measuring the left ventricular diastolic area is the left ventricular short axis view from the mid transgastric acoustic window. This view has been shown to be predictive of the LVEDV. The area is converted into left ventricular end-diastolic volume. Left ventricular end-diastolic volume is the amount of blood in the heart’s left ventricle just before the heart contracts. While the right ventricle also has an end-diastolic volume,.
End-diastolic volume is a useful indicator of a person’s heart health. Doctors use end-diastolic volume to estimate preload and calculate the heart’s stroke volume and ejection fraction.
Normal (reference) values for echocardiography, for all measurements, according to AHA, ACC and ESC, with calculators, reviews and e-book.
In cardiovascular physiology, end-diastolic volume (EDV) is the volume of blood in the right or left ventricle at end of filling in diastole which is amount of blood present in ventricle at the end of diastole. [1]Determining the left ventricular (LV) end-diastolic volume index (EDVI) is essential to evaluating LV function. LV EDVI—the volume of blood in the LV at end load filling indexed for body surface area (ml/m 2)—may be quantified, either manually or automatically, using cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) software.Results: The normal ranges for LV end-diastolic volume measurements after adjustment to body surface area (BSA) were 62-120 ml for males and 58-103 ml for females. LV mass indexed to BSA ranged from 50-86 g for males and 36-72 g for females.

The end-diastolic volume is an essential parameter used for the assessment of cardiac function, namely the calculation of the respective stroke volumes and ejection fraction and the estimation of left or right ventricular preload. It has a central role in the diagnosis of many cardiac conditions.ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC ASSESSMENT OF LV FILLING PRESSURES AND DIASTOLIC DYSFUNCTION GRADE. The key variables recommended for assessment of LV diastolic function grade include mitral flow velocities, mitral annular e0 ve-locity, E/e0 ratio, peak velocity of TR jet, and LA maximum volume index (Figure 8B).The LV volume point on the loop is the end-systolic (i.e., residual) volume (ESV). When the LVP falls below the left atrial pressure, the mitral valve opens (point 4) and the ventricle begins to fill.
what is Lv diastolic volume
lv jewelery
lv inspired swimsuit
Learn more about the permitting process and apply online or in person. You can apply for a permit. Get all trade permit applications and signs forms here. Find electrical, plumbing and mechanical applications and forms. Get translated trade permit applications.
lv end diastolic volume|Lv stroke volume 4c al